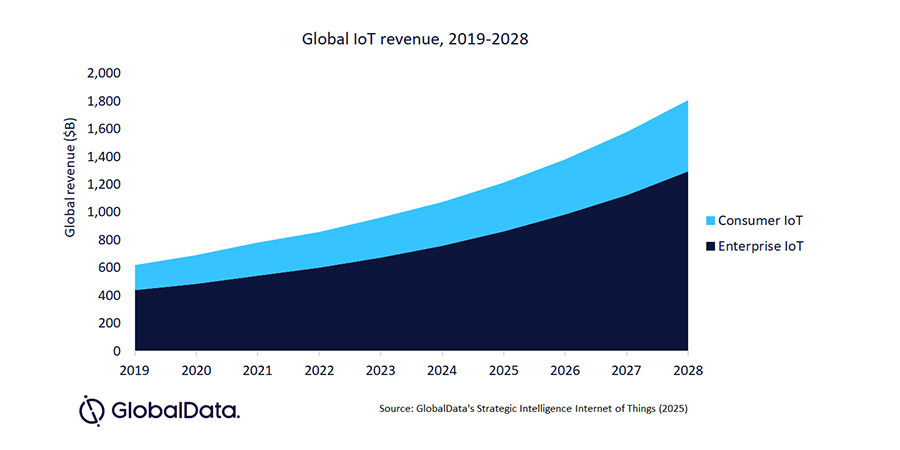
The global Internet of Things (IoT) market is expected to grow at a rate of 13.5% annually, reaching USD 1.8 trillion in revenue by 2028, notably increasing from the USD 959.6 billion recorded in 2023. This growth is being fueled by the increasing use of IoT in businesses and is supported by technologies such as 5G and artificial intelligence (AI). However, challenges such as security issues and differing standards need to be addressed to achieve widespread adoption and success.
Latest: Nokia Deploys First Lunar Cellular Network
GlobalData's recent report, “Internet of Things” indicates that enterprise IoT will contribute 72% of market revenue by 2028, an increase from the 70% achieved in 2023, while the consumer segment's share will decline from 30% in 2023 to 28% in 2028. New wireless technologies on land and in space will also provide more options for IoT connectivity. Improved 5G technology now supports IoT applications that require less complexity, lower costs, and reduced power consumption.
New Access Technologies and Integration
5G-satellite non-terrestrial networks (NTN) is a new access technology that will allow devices in remote areas to transmit and receive data via satellites. These new access technologies are suitable for devices needing continuous connectivity and long battery life but not requiring all of 5G’s features, such as higher bandwidth and lower latency.
AI is becoming increasingly important in driving IoT growth. The concept of Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) involves integrating AI into IoT devices, software, and services. By combining data from connected sensors and AI, automated operations and predictive maintenance are supported. AI can operate in the cloud, directly on IoT devices with some limitations, or on both the cloud and the device. William Rojas, Research Director at GlobalData, noted that AIoT technologies, along with new wireless access technologies, will further boost IoT adoption in both the business and consumer sectors.
As cloud analytics processing capabilities expand, deployments that previously used only one type of IoT sensor are now incorporating a wider range of sensors. Furthermore, security remains a significant concern for IoT implementations. The lack of unified security standards and the weak security of many IoT devices could hinder further IoT adoption. Despite industry efforts, there are no universally accepted IoT security standards.
Many IoT devices lack the computing power to run effective security software, making them, and the networks they connect to, vulnerable to cyberattacks. Rojas emphasized that IoT is a digital ecosystem comprising interconnected connectivity and data layers that collect, store, and process data from IoT sensors. Embedded AIoT can help enhance security at the IoT device level. In contrast, for tasks requiring heavy computing resources with low latency, edge computing is the preferred option.
IoT in Asia:
Foreign Investment Surges in Vietnam's Expanding IoT Market
Juniper Research Predicts 150% Surge in IoT-Connected Satellites by 2029